Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
What is Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM)?
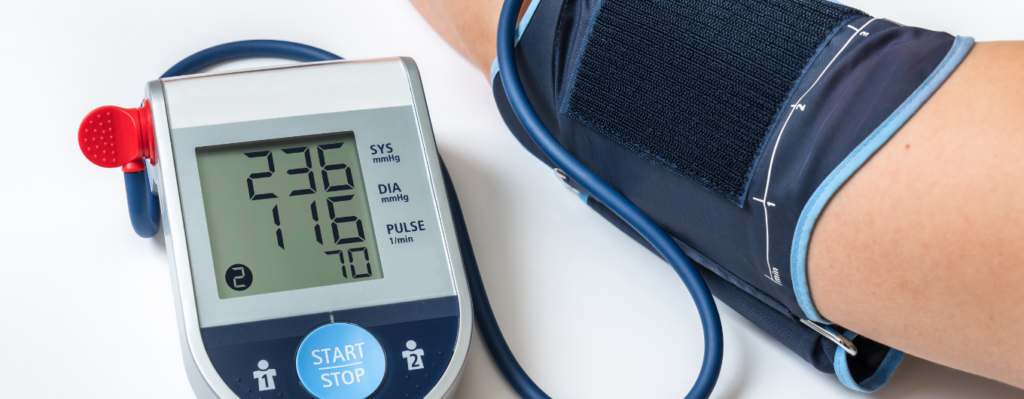
ABPM is a method of monitoring blood pressure over a 24-hour period using a portable device. The device automatically measures and records your blood pressure at regular intervals throughout the day and night, providing a more comprehensive picture of your blood pressure compared to a single reading in a doctor’s office.
Why is ABPM used?
ABPM is used to diagnose and monitor high blood pressure (hypertension). It helps identify cases of “white coat syndrome” (elevated blood pressure only in a clinical setting) and assess nighttime blood pressure, which can be an important indicator of cardiovascular risk.
How is ABPM performed?
The patient wears a cuff on their arm connected to a portable device that measures blood pressure at regular intervals (usually every 15–30 minutes during the day and every hour at night). The device is typically worn for 24 hours and then removed for analysis.
What are the benefits of ABPM over regular blood pressure measurements?
ABPM provides a more accurate assessment of a person’s blood pressure throughout the day, accounting for variations due to activity, stress, and sleep. It also allows for detection of abnormalities like nighttime hypertension or fluctuations that may not be captured during a single visit to the doctor.
Are there any risks or side effects with ABPM?
ABPM is generally safe, but some people may find the cuff uncomfortable or inconvenient, especially while sleeping. The frequent inflation of the cuff might also cause temporary discomfort or bruising. There are no significant long-term risks associated with ABPM.
