Holter Monitoring
What is Holter Monitoring?
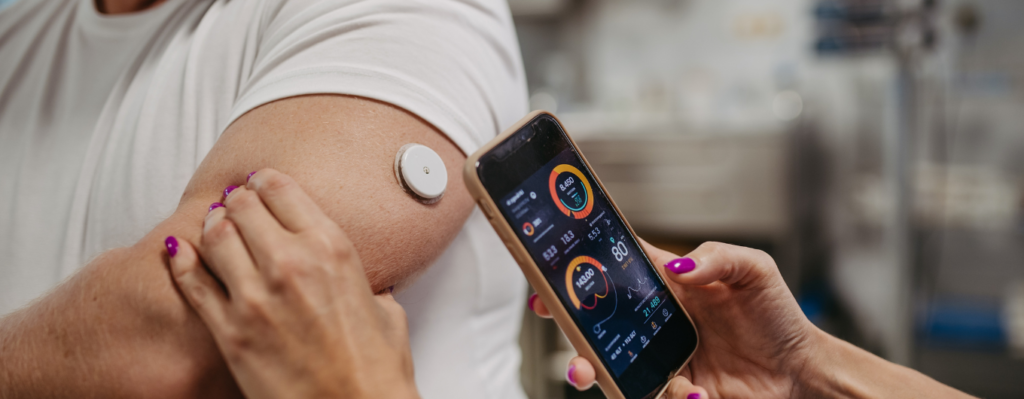
Holter Monitoring is a continuous test that records your heart’s electrical activity (ECG) over a 24-48 hour period. The patient wears a small, portable device called a Holter monitor, which tracks heart rhythm throughout normal daily activities, providing valuable insights into heart health.
Why is Holter Monitoring used?
It is used to detect irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), assess the cause of symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, or palpitations, and monitor heart conditions like atrial fibrillation, heart attack recovery, and effectiveness of heart medications or pacemakers.
How is Holter Monitoring performed?
During the test, electrodes are attached to the patient’s chest and connected to a small, portable device. The device records the heart’s electrical activity over a specified period, typically 24 or 48 hours. The patient is advised to continue with normal activities, such as walking, working, or sleeping, during the monitoring period.
What should I do during Holter Monitoring?
You should go about your normal daily activities, but it’s important to avoid excessive sweating, showering, or bathing, as water may interfere with the monitor. You may also be asked to keep a diary of activities and symptoms during the test to help correlate any changes in your heart rate with specific events.
Are there any risks or side effects with Holter Monitoring?
Holter Monitoring is non-invasive and generally safe with minimal risks. Some people may experience skin irritation or discomfort from the adhesive electrodes. There is no significant risk of electrical shock, as the device simply records data rather than transmitting any electrical current to the body.
